READY TO GET STARTED?
REQUEST A FREE ESTIMATE
Fill out the form below or call (888) 466-7849 for a free, no-obligation estimate.

The sun is shining, the warm breeze is blowing, you’ve got your feet up, unwinding from the week, when…OUCH! That moment of relaxation you’ve been waiting for was suddenly interrupted by a painful mosquito bite. At this point you’re annoyed, thinking about going back inside to avoid more bites, or wondering if you should make an appointment with your doctor to check for Zika or West Nile. What a summer bummer!
Mosquitoes not only pose serious risks for your family, but pets are a target too. Heartworms are parasites transmitted to dogs and cats through mosquito bites, that live in pets’ bloodstream, lungs and heart, and can cause serious, even deadly, side effects.
Don’t let mosquitoes suck the life out of your summer. Protect family and pets and take back your yard with these easy mosquito bite prevention tips:
Mosquitoes breed in areas with stagnant, standing water like fountains and water features, toys, buckets, outdoor pet bowls, bird baths, clogged gutters, vases, flowerpot saucers, old tires or tire swings, rain barrels, trash cans and trash can lids, tarps, kiddie pools, and pool covers. The best way to prevent mosquito bites is to remove these items/areas and to treat your yard with mosquito control products. This is included in a monthly mosquito reduction program and is guaranteed to drastically reduce the number of mosquitoes in and around your yard.
One of the best ways to prevent Zika and other mosquito-borne diseases is to use skin-applied insect repellent when you’re going to be outside. Formulas that contain DEET and picaridin were found to be most effective at preventing mosquito bites (and those with natural plant oils least effective), according to Consumer Reports.
If you really want to further prevent bites, keep arms and legs covered when outdoors with light-colored, loose clothing. Sometimes this can be just as uncomfortable as getting bitten, though, with the scorching summer heat. If you leave skin exposed, be sure to reapply insect repellent often (especially if you’ll be swimming).
Consider using fans in areas you’ll be hanging out this summer – on decks, patios, around pools, etc. Mosquitoes are weak fliers so the winds from fans will make it hard for them to get close enough to bite.
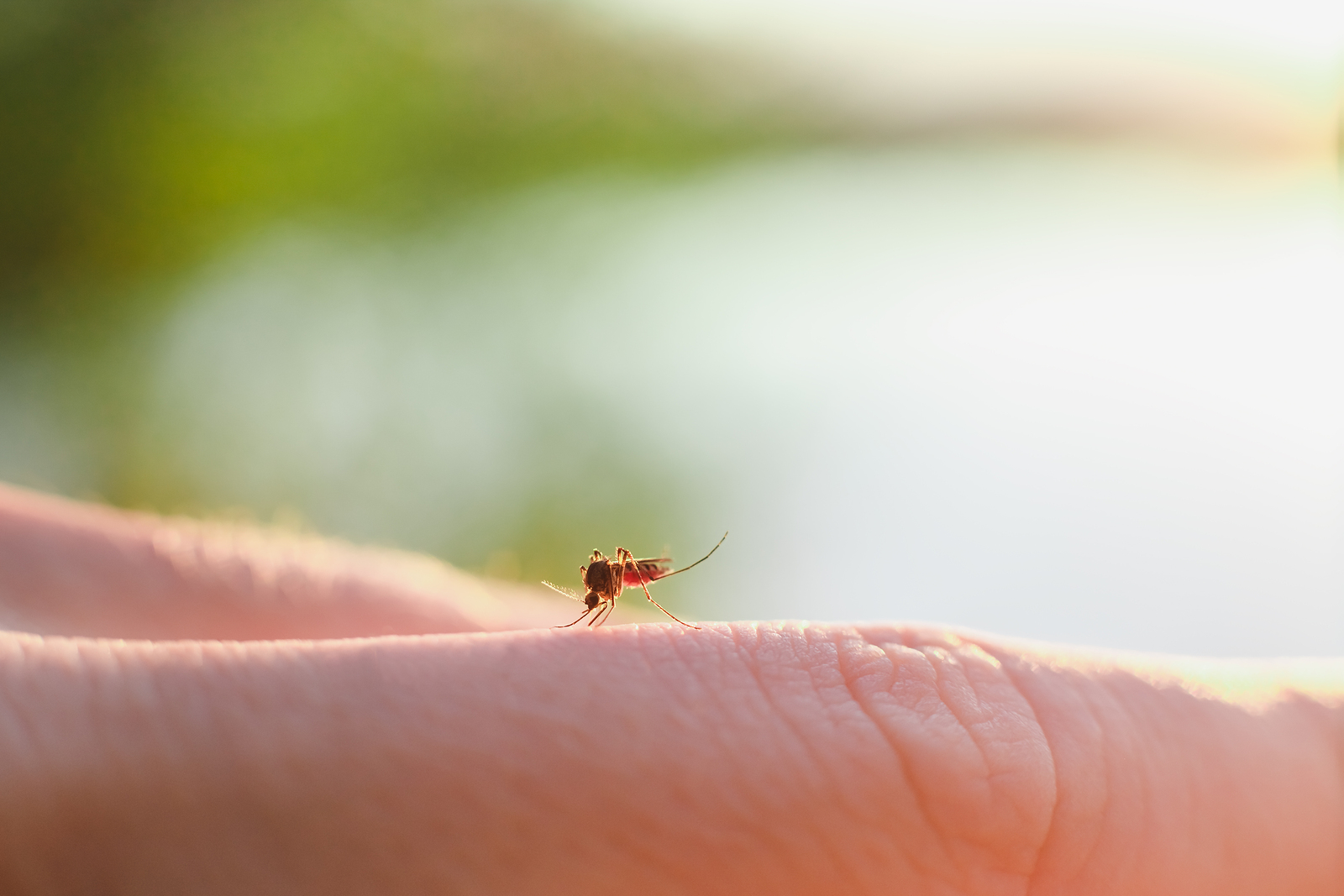

Mosquitoes are known carriers of several viruses, transmitting disease and parasites to people and animals that come in contact with them via painful bites. While some of these diseases don’t pose serious health risks, others can be deadly (over one million people die each year from mosquito-borne diseases, according to the AMCA!). Here are 3 common mosquito diseases you should be cautious of this summer:
First discovered in 1947, Zika, a mosquito-borne virus, originated in Uganda, Africa. Shortly after, outbreaks of Zika were detected throughout tropical areas in Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Pacific Islands, according to the CDC. Now, mosquitoes carrying Zika have been identified in many countries, including the U.S.
Primarily transmitted by the Aedes species, infected mosquitoes can spread Zika to humans and animals through bites. These mosquitoes are active during daytime and evening hours. Zika can also be sexually transmitted from one infected partner to another, from pregnant women to unborn babies, and through blood transfusions.
Common symptom of Zika include rash, fever, joint and muscle pain, headache, and/or red eyes and can last for up to a week, but many infected won’t show any symptoms at all. Zika is dangerous specifically for pregnant women as it can cause birth defects, a condition called Microcephaly, in fetuses. This can cause brain and eye defects, hearing deficits, and impair growth.
Because there’s currently no vaccine to treat and/or cure Zika, the best way to protect yourself is by preventing mosquito bites. Keep arms and legs covered in loose, light-colored clothing when outdoors and use insect repellent. Repair or replace missing or damaged window and door screens at home and keep them closed as often as possible. Control mosquito populations around your home by getting rid of adult mosquitoes as well as reducing mosquito reproduction with home mosquito treatments from a licensed pest control company. Most companies offer eco-friendly mosquito treatment options that are family and pet-friendly, if having your yard treated with chemicals is a concern. If pregnant, the CDC advises to avoid traveling to countries with known Zika outbreaks – see the list here – and refrain from unprotected sex.
Check with your doctor to get tested. To minimize symptoms, drink lots of fluids, get plenty of rest, reduce fever or pain with over-the-counter pain medicines (avoid aspirin), and prevent additional mosquito bites. If you’re bitten by a mosquito once infected, you can pass Zika to other mosquitoes, who will then infect someone else – increasing the spread of Zika. If you’re pregnant and suspect you have Zika, contact your physician immediately.
The first occurrences of West Nile in the U.S emerged in New York in 1999 with 62 confirmed cases and 7 human deaths, according to the AMCA. West Nile virus is a mosquito-borne virus carried by many different mosquitoes, one of the most common being the Culex species.
West Nile is most often transferred from birds to mosquitoes, and then from mosquitoes to humans and animals through bites.
Symptoms may develop 3-14 days after bitten. Typically only 20% of people infected with West Nile virus will experience symptoms which include headache, body aches, and fever and usually last a week or less. Rarely, the virus develops into West Nile encephalitis which can cause high fever, neck stiffness, disorientation, coma, muscle weakness, convulsions, paralysis, and sometimes death. This is most common in people over the age of 50.
Like Zika, there is no vaccine for West Nile virus. Prevent the virus by preventing mosquito bites.
See your doctor. A blood test can determine if you’re infected with West Nile virus. If symptoms are severe, hospitalization may be necessary.
Dengue, a mosquito-borne virus, is the leading cause of illness and death in the tropics and subtropics according to the CDC (400 million people infected each year). While it rarely occurs in the U.S., it’s important to be aware of dengue while traveling to popular tourist destinations like Puerto Rico, parts of Central and South America, Southeast Asia, and the Pacific islands. Dengue is carried by the Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquito species which are found throughout the world.
Mosquitoes carrying dengue infect humans through bites and infected humans can infect other mosquitoes, when bitten.
Most cases of dengue in the U.S. were acquired through travel abroad. Symptoms include severe headache, high fever, eye pain, joint pain, muscle pain, and rash. Severe cases can cause stomach pain, vomiting, difficulty breathing, and bleeding from gums and/or nose.
Mosquito bite prevention is key when traveling to areas with known dengue outbreaks as there is no vaccine for dengue or medications to treat it. It’s especially critical for people with dengue to avoid mosquito bites so the disease isn’t spread from person to another mosquito.
If symptoms are mild, lots of rest and fluids are recommended. For more severe symptoms, contact your health care provider immediately.

With every passing week, Zika becomes more dangerous and is spreading to new areas. Until now, Zika has been a threat mostly to pregnant women, their partners, or couples that are trying or planning to conceive due to the birth defect Microcephaly that Zika can cause. And while the virus does pose health risks much like other viruses – fever, rash, joint pain, headache – it appeared somewhat asymptomatic, other than recent reports that links Zika to the eye infection uveitis.
Now researchers are conducting experiments with findings that show an alarming relationship between Zika and serious long-term effects on the central nervous system of adults. The study, published Thursday in Cell Stem Cell, was performed on mice and found that Zika virus appears to cause cell death in neural stem cells and also hinders their ability to regenerate. The infected mice experienced a decrease in cell population in 2 areas of the brain that was twenty times more pronounced compared to other brain regions.
“Ours is the first study to look at Zika infection in the adult brain in an animal model. What we found was quite striking and dramatic. The stem cell population are highly vulnerable to Zika,” says Dr. Joseph Gleeson, lead author of the study. “In a sense, it’s the exception that proves the rule. It’s not so much the age of the person but the type of cells themselves that are vulnerable and not vulnerable.”
According to Gleeson, the study does come with limitations but clearly suggests that more research is needed and there are more questions to be answered.
For now, the best way to protect yourself and your family from Zika is with mosquito bite prevention. Use insect repellent with DEET when outdoors, keep your arms and legs covered in light-colored, loose clothing, keep doors and windows closed, and contact your local exterminator for mosquito control treatments around your home.
The first cases of locally transmitted Zika virus were reported this week in Florida. On July 29th, 4 people infected with Zika virus in Miami reportedly were bitten by mosquitoes within the city. On August 1st, that number grew from 4 to 14 infected. Until now, all reported cases of Zika in the United States have been linked to those who recently travelled to countries with known Zika transmissions.
Due to the recent developments, the Centers for Disease Control are warning pregnant women and their partners to avoid traveling to Miami and surrounding areas. Zika virus is extremely dangerous to unborn babies, potentially causing a condition known as Microcephaly, a birth defect characterized by abnormally small heads and underdeveloped brain function. Pregnant women and/or their partners that have recently travelled to the area (on or after June 15th) should be tested immediately for Zika virus and those living in and around Miami should exercise strict mosquito bite prevention and avoid unprotected sex.
As for the rest of the country, the risk of contracting Zika from mosquitoes isn’t an immediate threat since mosquitoes carrying Zika do not travel far (a mile or less in their lifetime). BUT, because symptoms of Zika often go unnoticed, those that have recently traveled to the area and may have Zika are likely to pass the virus on to sexual partners, OR could spread the virus to another mosquito if bitten. In turn, that mosquito could then transmit Zika to other people.
Because of its unpredictability, practicing mosquito bite prevention in any warm, humid climate (within the US and when traveling abroad) is key – especially for pregnant women and those planning to become pregnant. Use an insect repellent with DEET when outdoors, keep arms and legs covered with light-colored, loose clothing, stay away from areas with stagnant, standing water, and consider a home mosquito control program by an exterminating company.

By now we know that Zika Virus, a mosquito-borne disease, carries some serious health threats and risks, previously thought to be most dangerous for pregnant mothers and their unborn babies. If bitten by the Aedes aegypti mosquito carrying Zika, an unborn baby could potentially be born with a serious birth defect called Microcephaly, causing abnormally small heads and impaired brain function.
Now Zika Virus is also being linked to and eye infection causing permanent blindness, reported by the New England Journal of Medicine last week. This Zika-induced eye infection, uveitis, can cause glaucoma, cataracts and loss of vision.
If you’ve recently traveled to countries with documented Zika transmission – like Brazil, parts of the Carribbean and Central America, Mexico, and the Pacific Islands – see an ophthalmologist. Potential signs and symptoms of an eye infection related to Zika Virus are eye redness, pain or sensitivity to light. If left untreated, uveitis can “cause irrevocable damage to the retina,” according to Dr. C. Stephen Foster, president of the Massachusetts Eye Research and Surgery Institution in Waltham.
Protect yourself from mosquito bites by using bug repellent with DEET and keeping your arms and legs covered with loose-fitting long sleeves and pants (find out more about mosquito bite prevention here). Pregnant women or women expecting to become pregnant should avoid traveling to these countries all together. The same applies to men that are trying to conceive with their partner; Zika Virus can be sexually transmitted from men to women.
Those planning to travel to Rio, Brazil for the upcoming 2016 Summer Olympics are especially at risk. At least 4-6 weeks prior to your trip, talk to your doctor about vaccinations and medicines recommended for travel to Brazil. It’s also a good idea to purchase travel health and medical evacuation insurance, according to the CDC, and stay up to date with travel warnings and breaking news in that area. While visiting Rio, mosquito bite prevention is key to reducing your risk of Zika and other mosquito-born diseases. Wear mosquito repellent with DEET around the clock, avoid areas of standing or stagnant water, and wear loose, light-colored clothing that covers arms and legs. And since Zika can be sexually-transmitted, avoid unprotected sex during travel and for at least 8 weeks after. The CDC recommends that pregnant women not go to the Olympics.